Content Lifecycle Management
Manage Your Content Lifecycle
Monitor Your Mission-Critical Data
Easily review the status of all of your company’s content from a single, comprehensive dashboard.
Reduce Cyberattack Surface
Delete or archive obsolete content that could be leveraged by cyberattackers or malicious insiders.
Streamline Compliance
Comply with global and regional data retention regulations that impact your business.
Content Lifecycle Management Capabilities
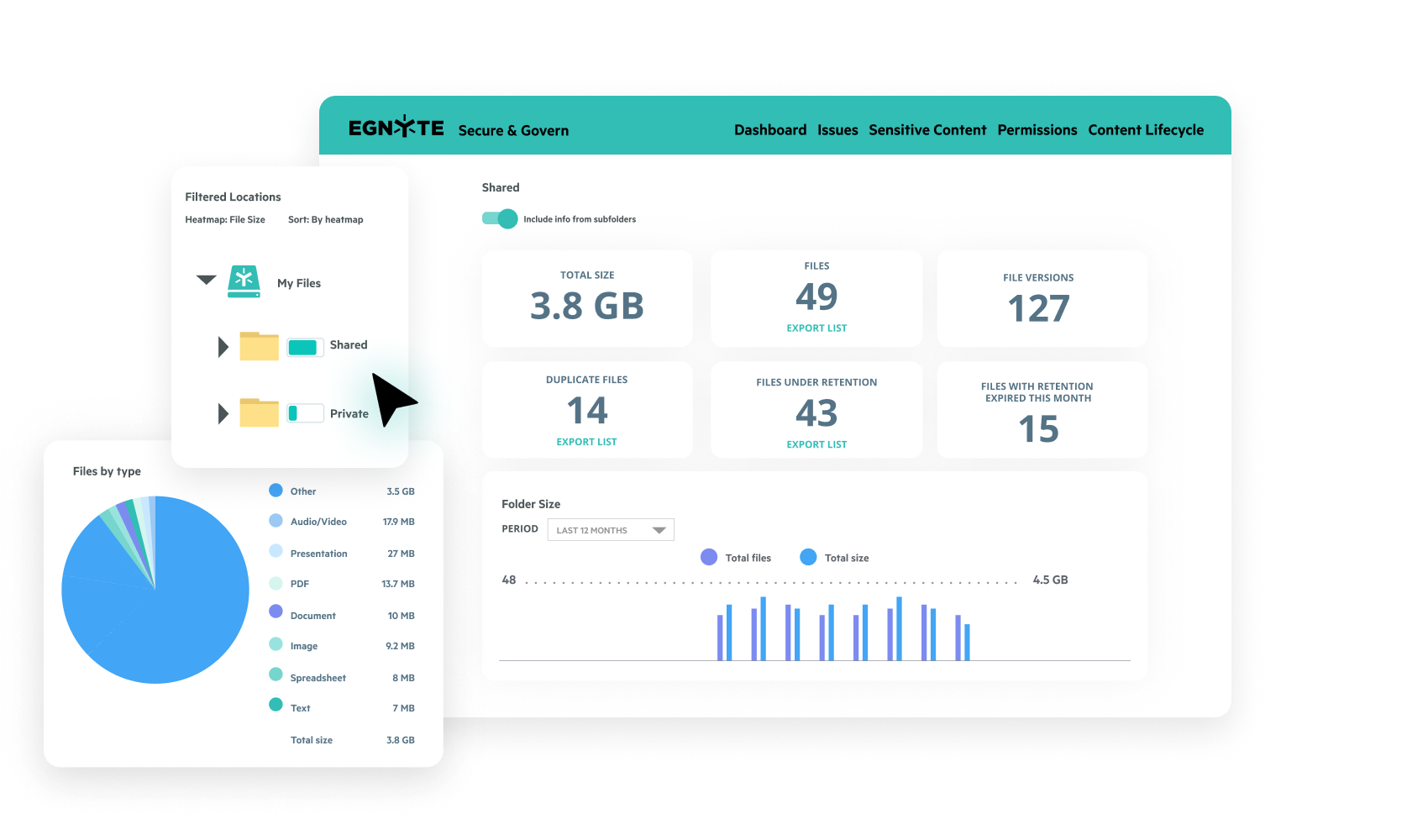
Content Lifecycle Dashboard
- See where your mission-critical content resides, across all data repositories
- Easily identify duplicate files, and files under data retention
- Take immediate action to archive or delete redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) content
- Align dashboard review with security compliance management requirements pertinent to your organization
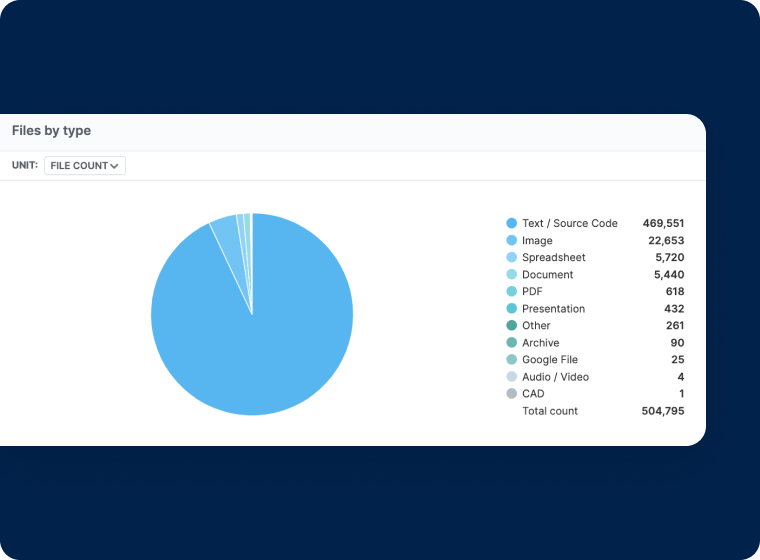
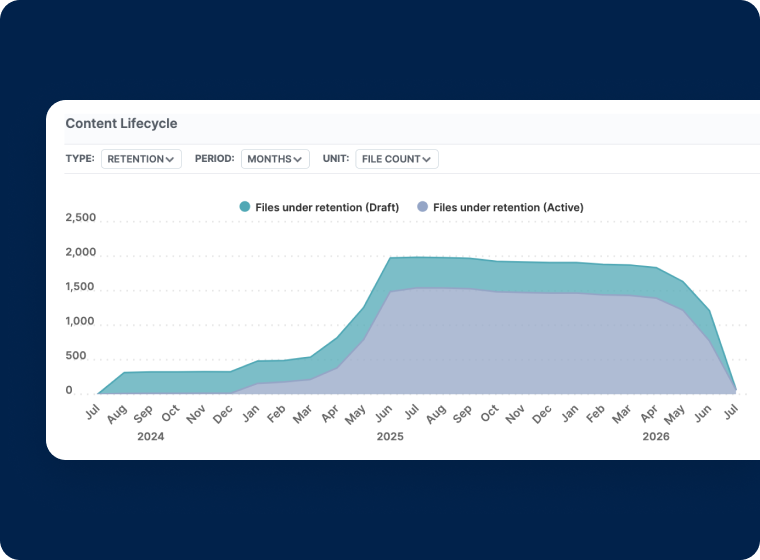
Centralized Administration
- Get a comprehensive view of stored files, by file type
- Increase productivity by giving users access to the most current data available
- Centralize retention policies organizationally to prevent accidental data deletion
- Reduce storage costs for data that isn’t actively being accessed
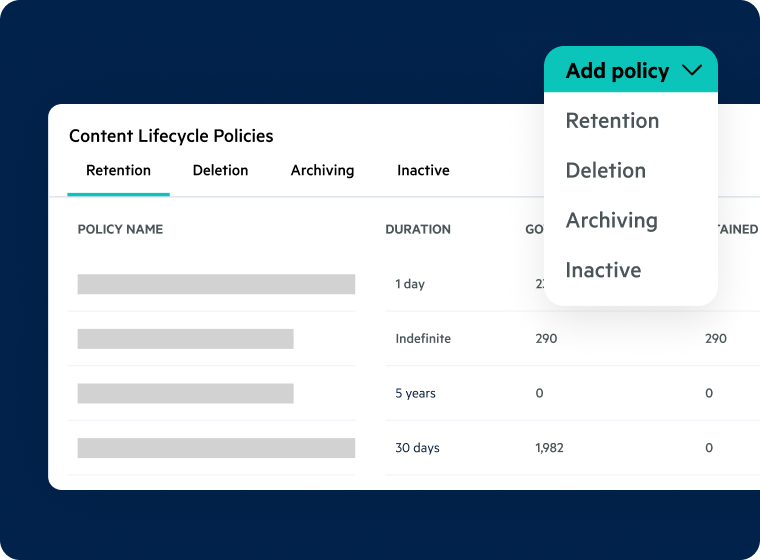
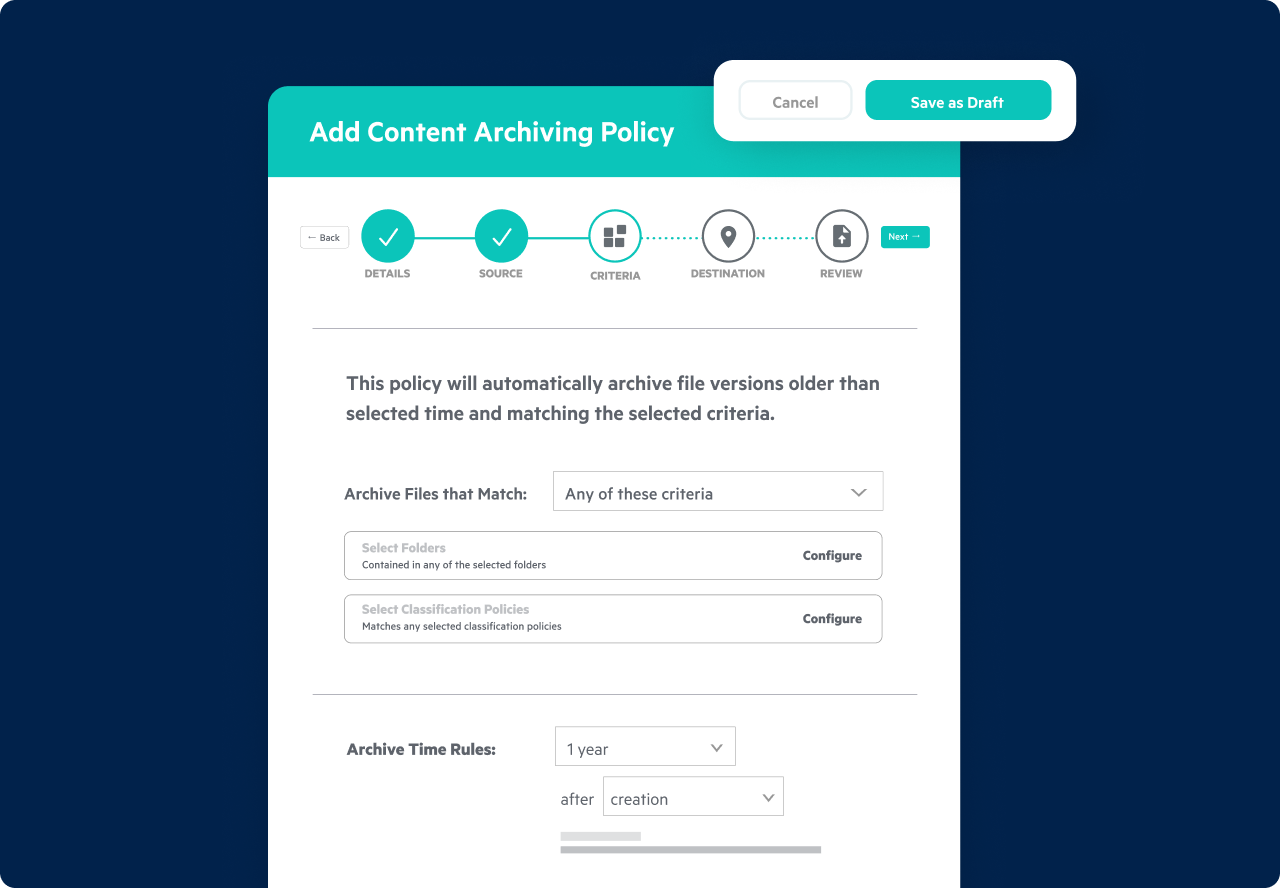
Compliant Data Retention and Archival
- Create retention and archival policies aligned with data lifecycle program management guidelines
- Select from numerous standard lifecycle policies or create customized policies of your own
- Leverage Egnyte's Artificial Intelligence (Al) expertise to identify content subject to important policies
- Apply and enforce policies in conjunction with regulatory and business requirements
Hear From Our Customers
See Egnyte Content Lifecycle Management in Action
Improve users’ productivity and manage mission-critical content more effectively by:
- Enabling secure collaboration
- Creating workflows for key project participants
- Proactively deleting or archiving data that is no longer needed by the business
You Might Also be Interested In
FAQs
Content Lifecycle Management (CLM) refers to the process of managing digital content from creation and users’ initial collaboration to classification, retention, and secure disposal (for example, the content’s archival or deletion). CLM ensures that data remains compliant, accessible, and organized throughout its lifecycle. Effective CLM reduces storage costs, mitigates data sprawl, and strengthens governance and data security posture, making it essential for regulated industries and enterprises that handle high volumes of unstructured data.
To explore how organizations are addressing data sprawl and improving governance, watch the on-demand webinar: Governance in a Data Sprawl World.
Organizations often struggle with data sprawl across their content storage repositories, lack of visibility into aging or redundant files, inconsistent retention policies, and non-compliance with regulatory standards. Without a centralized CLM strategy, businesses are susceptible to security breaches, excessive storage costs, and audit failures. Automating CLM helps address these challenges by enforcing retention rules, improving data classification, and promoting policy-based governance.
CLM enforces consistent retention, archival, and deletion policies across all repositories, ensuring that sensitive data is properly governed. It helps organizations meet compliance mandates such as HIPAA, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), GDPR, and/or FINRA by providing auditable controls, access logs, and automated file disposition. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhances enterprise-wide data governance.
By automating content classification and archiving obsolete files, CLM streamlines access to the most current and relevant information. Teams spend less time searching for documents and more time collaborating on active files. CLM also ensures content is appropriately shared and retained, which enhances productivity while reducing the risk of working on outdated or unauthorized versions.
When a retention policy expires, the system can automatically archive, delete, or flag files for review based on the configured rules. This reduces manual intervention, lowers storage costs, and ensures that content does not remain longer than necessary, helping meet compliance requirements and minimize legal exposure.
Only authorized administrators can create, edit, or delete retention policies within a CLM system. This ensures that governance rules are enforced consistently and prevents end users from bypassing compliance protocols. Role-based access controls and audit logs help maintain policy integrity and transparency.